Erector Spinae Plane Block
When to block:
Patients presenting with:
• Rib fractures (3 or more)
• May consider in burns, shingles, transverse process fractures, chest tubes
Amount of anesthetic:
• ~15-20cc 0.5% bupivacaine
• Bupivacaine max dose: 2-2.5mg/kg (175mg/dose)
• Monitor patient on cardiac monitor for at least 60min (re LAST)
Where you put the probe and needle:
ORGANIZATION 1

• Position - sitting, prone or lateral decubitus
• Linear High Fq probe
• Use Sterile/Semi-sterile technique
• Place in longitudinal plane
• Probe marker to patient’s head
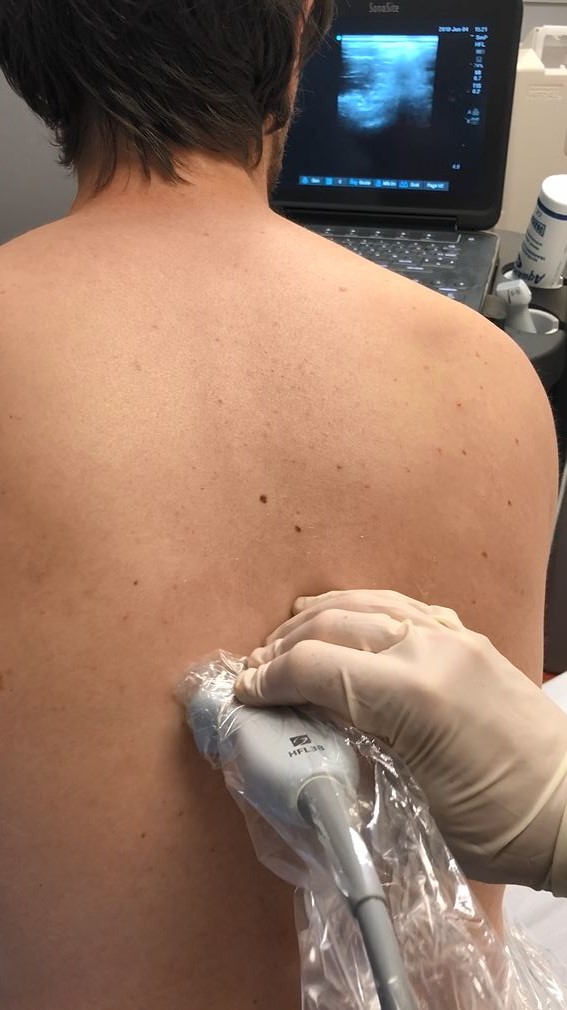

• Start by finding the Spinous Process midline
Identify the Transverse Process:
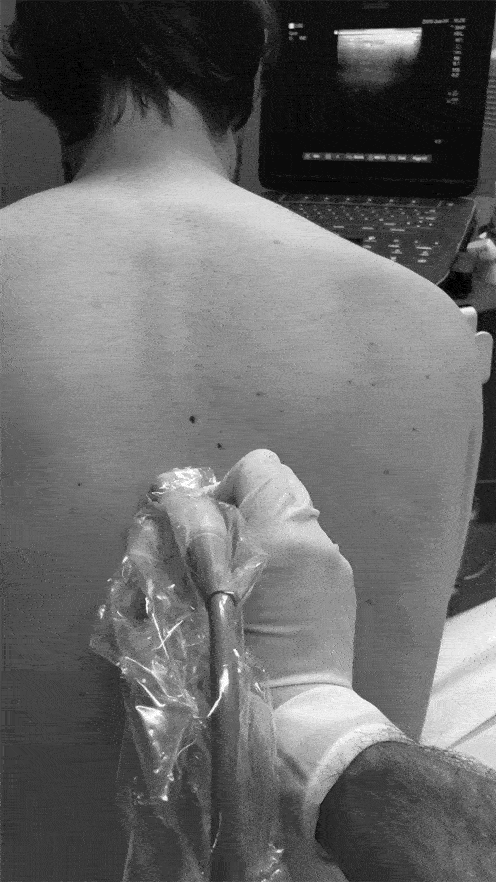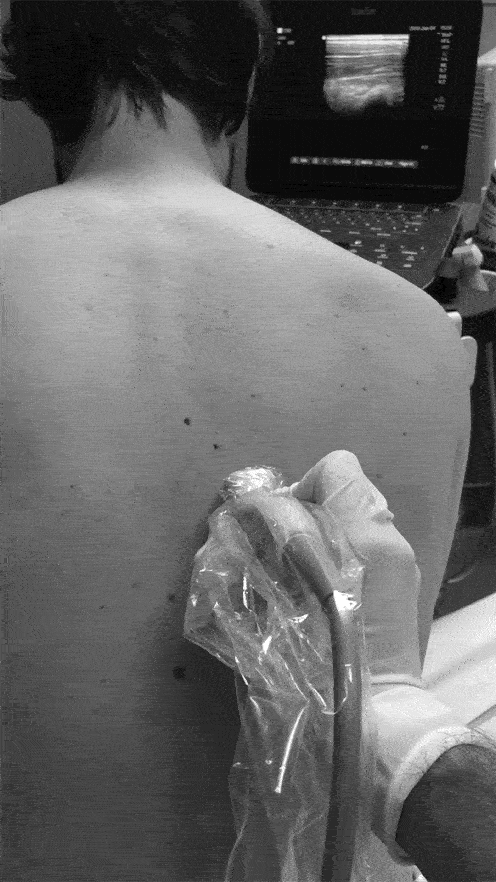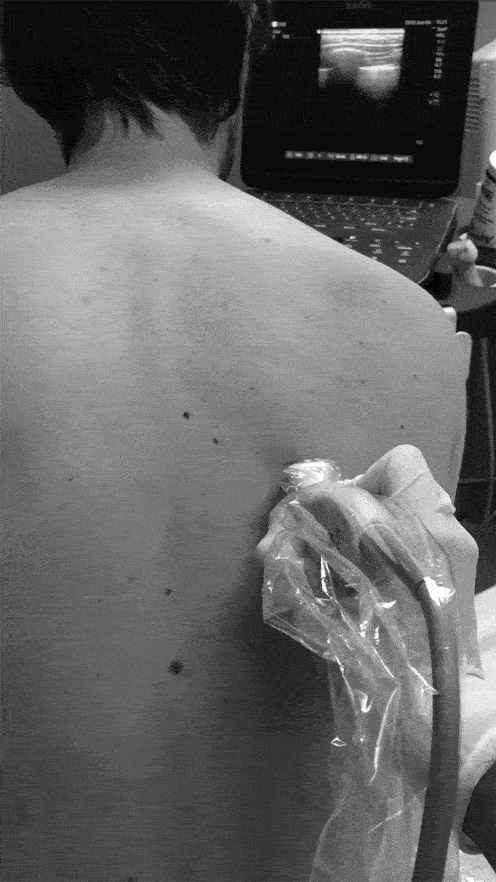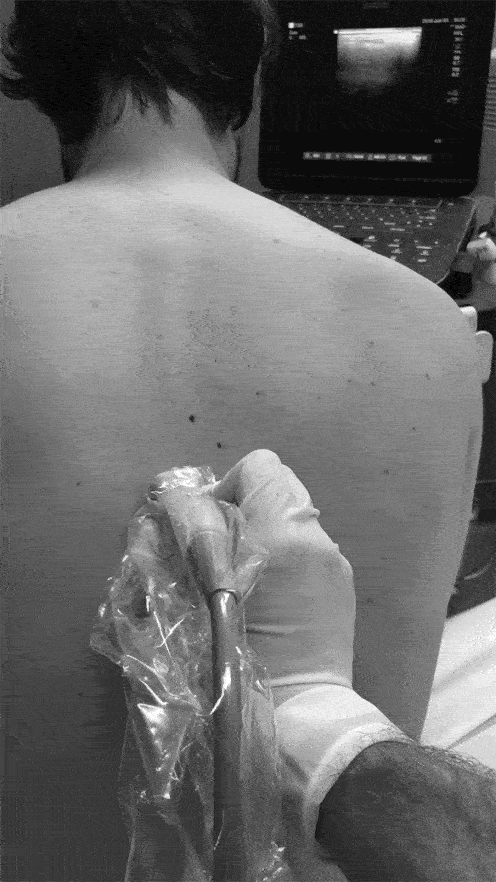
• The Transverse Process is ~3cm lateral to the Spinous Process

• View the Spinous Process midline then slide lateral to Lamina, and then Transverse Process (Transverse Process will be more superficial to Lamina and with a flatter top than more rounded Ribs)
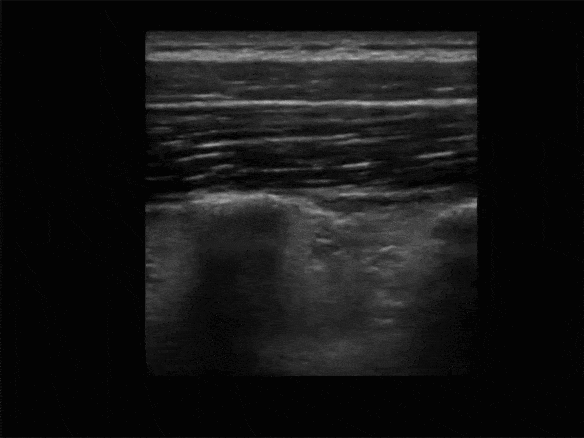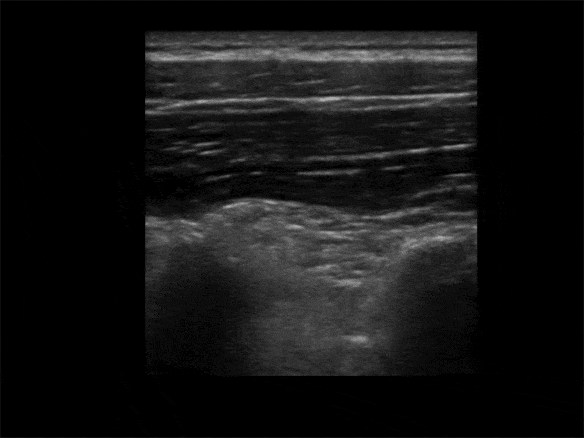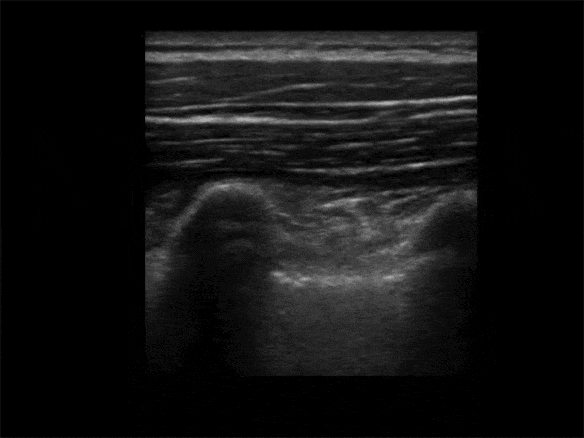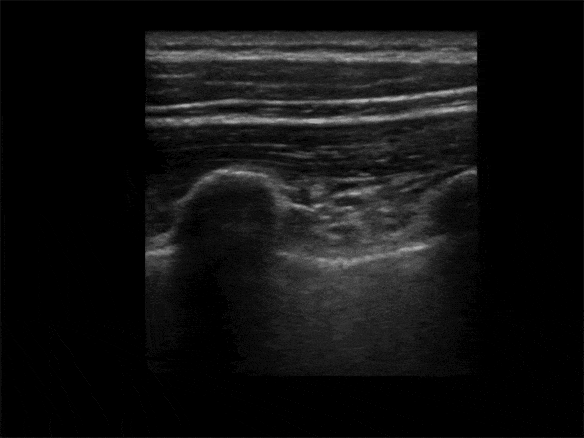
• The more rounded Rib is lateral of the Transverse Process
• Avoid the lungs (may see lung sliding lateral and deep)
Inject the anesthetic:
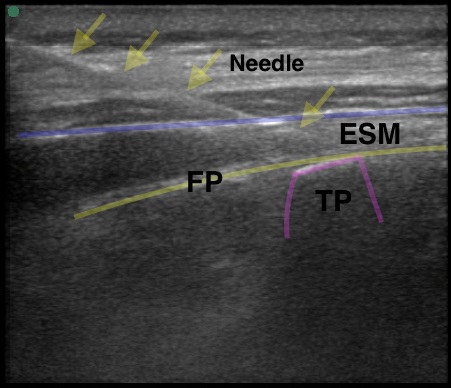
• Insert needle from above or below using in plane technique, always visualizing the needle tip

• Injecting anesthetic deep to the Erector Spinae muscle/plane
ORGANIZATION 2

• Position - sitting, prone or lateral decubitus
• Linear High Fq probe
• Use Sterile/Semi-sterile technique
• Place in longitudinal plane
• Probe marker to patient’s head


• Start by finding the Spinous Process midline

• The Transverse Process is ~3cm lateral to the Spinous Process

Identify the Transverse Process:
• View the Spinous Process midline then slide lateral to Lamina, and then Transverse Process (Transverse Process will be more superficial to Lamina and with a flatter top than more rounded Ribs)

• The more rounded Rib is lateral of the Transverse Process
• Avoid the lungs (may see lung sliding lateral and deep)

• Insert needle from above or below using in plane technique, always visualizing the needle tip

• Injecting anesthetic deep to the Erector Spinae muscle/plane
ORGANIZATION 3

• Position - sitting, prone or lateral decubitus
• Linear High Fq probe
• Use Sterile/Semi-sterile technique
• Place in longitudinal plane
• Probe marker to patient’s head


• Start by finding the Spinous Process midline
Identify the Transverse Process:

• The Transverse Process is ~3cm lateral to the Spinous Process

• View the Spinous Process midline then slide lateral to Lamina, and then Transverse Process (Transverse Process will be more superficial to Lamina and with a flatter top than more rounded Ribs)

• The more rounded Rib is lateral of the Transverse Process
• Avoid the lungs (may see lung sliding lateral and deep)
Inject the anesthetic:

• Insert needle from above or below using in plane technique, always visualizing the needle tip

• Injecting anesthetic deep to the Erector Spinae muscle/plane
ORGANIZATION 4

• Position - sitting, prone or lateral decubitus
• Linear High Fq probe
• Use Sterile/Semi-sterile technique
• Place in longitudinal plane
• Probe marker to patient’s head


• Start by finding the Spinous Process midline
Identify the Transverse Process:

• The Transverse Process is ~3cm lateral to the Spinous Process

• View the Spinous Process midline then slide lateral to Lamina, and then Transverse Process (Transverse Process will be more superficial to Lamina and with a flatter top than more rounded Ribs)

• The more rounded Rib is lateral of the Transverse Process
• Avoid the lungs (may see lung sliding lateral and deep)
Inject the anesthetic:

• Insert needle from above or below using in plane technique, always visualizing the needle tip

• Injecting anesthetic deep to the Erector Spinae muscle/plane
- Identify ulnar artery near wrist, ulnar nerve lies on ulnar aspect of artery!
- Helps to have shoulder abducted and external rotated as shown
- Slide proximal to find easiest access to nerve for in-plane injection

- Injecting anesthetic alongside ulnar nerve

- Ulnar nerve distribution in yellow

